- makeITcircular 2024 content launched – Part of Maker Faire Rome 2024Posted 2 weeks ago
- Application For Maker Faire Rome 2024: Deadline June 20thPosted 2 months ago
- Building a 3D Digital Clock with ArduinoPosted 7 months ago
- Creating a controller for Minecraft with realistic body movements using ArduinoPosted 7 months ago
- Snowflake with ArduinoPosted 8 months ago
- Holographic Christmas TreePosted 8 months ago
- Segstick: Build Your Own Self-Balancing Vehicle in Just 2 Days with ArduinoPosted 8 months ago
- ZSWatch: An Open-Source Smartwatch Project Based on the Zephyr Operating SystemPosted 9 months ago
- What is IoT and which devices to usePosted 9 months ago
- Maker Faire Rome Unveils Thrilling “Padel Smash Future” Pavilion for Sports EnthusiastsPosted 10 months ago
MIOpen and ROCm: AMD’s free, open-source deep learning softwares
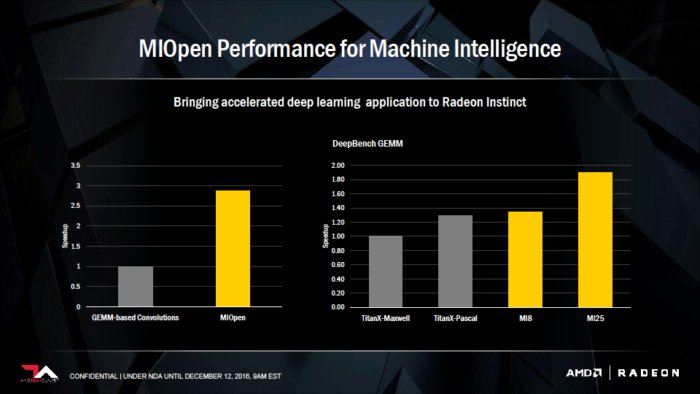
To support the new family of Radeon Instinct accelerators, AMD plans to roll out an open source library called MIOpen. It provides GPU-tuned implementations for standard routines such as convolution, pooling, activation functions, normalization and tensor format.
AMD will also launch the ROCm software platform, which the company said is optimized for accelerating deep learning frameworks such as Caffe, Torch 7 and Tensorflow.
Among the sectors AMD is targeting with Instinct, MIOpen and ROCm, are self-driving cars, smart homes, autopilot drones, personal robots, financial services and security.
“Radeon Instinct is set to dramatically advance the pace of machine intelligence through an approach built on high-performance GPU accelerators, and free, open-source software in MIOpen and ROCm,” said Raja Koduri, head of AMD’s Radeon Technologies Group.
AMD said its new Instinct accelerators are aimed at enabling customers to better use and understand the vastly expanding volumes of data being generated by a wide range of applications and devices. The new technologies are designed to provide a blueprint for an open software ecosystem for machine intelligence, helping to speed inference insights and algorithm training.
The Radeon Instinct lineup includes three different accelerators: two for inference applications and one designed for deep learning training:
– MI6 inference-focused accelerator, based on the Polaris GPU architecture, will offer a peak FP16 performance of 5.7 teraflops and is passively cooled.
– MI8 inference accelerator is based on the Fiji architecture and promises a peak FP16 performance of 8.2 teraflops
– Radeon Instinct MI25, is optimized for deep learning training and is built on AMD’s Vega GPU architecture. It is passively cooled.