- makeITcircular 2024 content launched – Part of Maker Faire Rome 2024Posted 2 weeks ago
- Application For Maker Faire Rome 2024: Deadline June 20thPosted 2 months ago
- Building a 3D Digital Clock with ArduinoPosted 7 months ago
- Creating a controller for Minecraft with realistic body movements using ArduinoPosted 7 months ago
- Snowflake with ArduinoPosted 8 months ago
- Holographic Christmas TreePosted 8 months ago
- Segstick: Build Your Own Self-Balancing Vehicle in Just 2 Days with ArduinoPosted 8 months ago
- ZSWatch: An Open-Source Smartwatch Project Based on the Zephyr Operating SystemPosted 9 months ago
- What is IoT and which devices to usePosted 9 months ago
- Maker Faire Rome Unveils Thrilling “Padel Smash Future” Pavilion for Sports EnthusiastsPosted 10 months ago
Measuring 20V signals on an Arduino Uno with a quantizer
As we know, Arduino Uno includes a 10-bit ADC (analog-to-digital converter) inside its ATmega328p, which takes a signal between 0 and 5V and produces a digital value that varies from 0 to 1023. However, attempting to measure any voltage above 5V will cause some less than desirable results, such as creating magic smoke and destroying the microcontroller. To get around this, some makers add a voltage divider that divides the input voltage by a predetermined factor. This solution reduces the resolution of the ADC, as a single step of the digital value corresponds to a greater voltage variation. To solve this problem, the YouTuber known as Techoyaki has come up with a new solution that can measure the entire range of values without reducing the resolution.
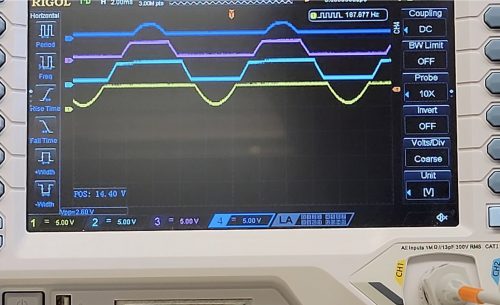
The circuit divides the 0V-20V range into four ranges (0V-5V, 5v-10V, 10V-15V and 15V-20V) translating them all into the 0-5V range. After that, these four obtained signals arrive at the Arduino’s four analog inputs, which add up the values to produce the equivalent of an ADC of nearly 12 bits, thus leading to values that fall between 0 and 4092 (1023 x 4).
The circuit is composed of four rail-to-rail operational amplifiers, and various resistors, which allow to limit the voltage obtained in the 0v-5v range and subtract a DC voltage value to effect the translation in the desired range.















