- makeITcircular 2024 content launched – Part of Maker Faire Rome 2024Posted 2 weeks ago
- Application For Maker Faire Rome 2024: Deadline June 20thPosted 2 months ago
- Building a 3D Digital Clock with ArduinoPosted 7 months ago
- Creating a controller for Minecraft with realistic body movements using ArduinoPosted 7 months ago
- Snowflake with ArduinoPosted 8 months ago
- Holographic Christmas TreePosted 8 months ago
- Segstick: Build Your Own Self-Balancing Vehicle in Just 2 Days with ArduinoPosted 8 months ago
- ZSWatch: An Open-Source Smartwatch Project Based on the Zephyr Operating SystemPosted 9 months ago
- What is IoT and which devices to usePosted 9 months ago
- Maker Faire Rome Unveils Thrilling “Padel Smash Future” Pavilion for Sports EnthusiastsPosted 10 months ago
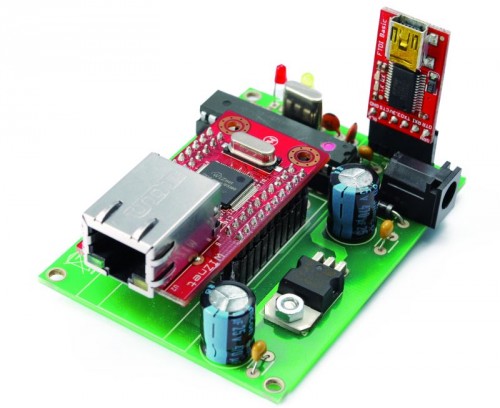
Arduino DDNS (Dynamic DNS)
This device captures the IP address of your network and it publish on site DynDNS.com. All without PC. It allow a remote access to your LAN even if the IP address of the connections changes.
For logistics reasons the provider can not assign a IP fixed for all users, so many users, especially private, work with a dynamic IP or public IP: in practice when they connect modem or router, to their connection is assigned an IP address that, when the connection will’be closed, can be used by other users. This makes impossible to contact a remote computer or device connected to a LAN Internet.
If you want to access to a device connected to your home LAN (so not with static IP) you must use a service like DynDNS, because every time you connect your ISP dynamically assigns a new IP address.
If you don’t want to use the software provided by DynDNS, and then leave the PC switched on continuously, the solution is this project.
Our device queries the site http://checkip.dyndns.com/ to know the IP currently used for the connection, and then publish your free account to www.dyndns.com instead of the computer acquired the new IP. Such a device therefore allows to locate a LAN connected to the Internet via a router or modem network.
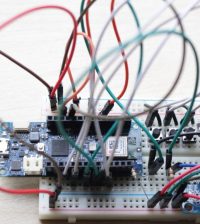
Our device is essentially a publisher of IP address. Everything is made from a circuit that incorporates an Ethernet interface WIZnet WIZ811MJ, managed by an Atmega328 microcontroller programmed with the Arduino bootloader, so it all works like an Arduino and you can use the Arduino IDE. The Atmega I/O PB2, PB3, PB4 and PB5 are dedicated to dialogue with the Ethernet module and provide a full four-wire SPI bus. The microcontroller is programmed using the special interface TTL / USB from SparkFun.
The main program sends the request to the IP address http://checkip.dyndns.com/ site. Now prepare the process of submitting to the site www.dyndns.com, which provides for the opening of a session onthe web page on, where will send data strings containing user name and password, thena string containing the Current IP connection. Cyclically the microcontroller check the IP to see if the address is changed, then, if it’s true, sends the new IP to www.dyndns.com
We use a dedicated circuit but the project can be replicated using an Arduino UNO and a Ethernet Shield.
Sketch Code for Arduino DDNS (Dynamic DNS)
/* DynDNS
created 2011
by Boris Landoni
This example code is in the public domain.
http://www.open-electronics.org
http://www.futurashop.it
*/
//http://username:password@members.dyndns.org/nic/update?hostname=yourhostname&myip=ipaddress
#include <Ethernet.h>
//#include <EthernetDNS.h>
#include <WString.h>
#include <EEPROM.h>
#define UPDATE_INTERVAL 30000 // if the connection is good wait 30 seconds before updating again - should not be less than 5
int ledR = 8;
int ledG = 9;
unsigned long pubblica=0;
byte mac[] = { 0x54,0x55,0x58,0x10,0x00,0x24 };
byte ip[] = { 192, 168, 0, 98 };
byte domainaddrip[]= { 208, 78, 70, 70 }; //http://checkip.dyndns.com/
byte ipAddr[4];
byte domaindydns[]= { 204, 13, 248, 112 }; // members.dyndns.org
char hostname[ ] = "xxxxxxx.getmyip.com";
char userpwdb64[ ] = "xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx"; //http://www.functions-online.com/base64_encode.html use-> username:password
String ipadsl = String(20);
String ipadslold = String(20);
String inString = String(51);
//Client client(server, 80);
const char* ip_to_str(const uint8_t*);
//void nameFound(const char* name, const byte ipAddr[4]);
Client client(domainaddrip, 80);
Client clientdyn(domaindydns, 80);
void setup()
{
pinMode(ledR, OUTPUT);
pinMode(ledG, OUTPUT);
Ethernet.begin(mac, ip);
//EthernetDNS.setDNSServer(dnsServerIp);
Serial.begin(9600);
Serial.println("*****************************************Start***************************************************");
delay(1000);
//risolviip();
//delay(1000);
}
void loop()
{
if (millis() < pubblica) pubblica = millis();
if ((millis() - pubblica) > UPDATE_INTERVAL){
//Serial.print("Passati ");
//Serial.print(UPDATE_INTERVAL);
//Serial.println(" ms");
Serial.print("tempo trascorso dall'accensione ");
Serial.println(millis());
Serial.println(pubblica);
pubblica = millis();
acquisisciip();
}
}
void acquisisciip()
{
int timeout=0;
int skip=0;
ipadsl="";
inString="";
digitalWrite(ledG, HIGH);
Serial.print("connecting to ");
//Serial.print(domain);
//Serial.print(" = ip ");
//Serial.println(ip_to_str(domainaddrip));
if (client.connect()) {
Serial.println("connected");
client.println("GET / HTTP/1.0");
//client.println("GET / HTTP/1.0");
client.print("HOST: ");
client.println("www.dyndns.com");
//client.println(ip_to_str(domainaddrip));
client.println();
} else {
Serial.println("connection failed");
}
while (!client.available() && timeout<50)
{
timeout++;
Serial.print("Time out ");
Serial.println(timeout);
delay(100);
}
while (client.available())
{
//Serial.println("client.available");
//if (client.available())
//{
char c = client.read();
//Serial.print(c);
skip++;
if (skip>220)
{
if ((inString.length())<50) inString.append(c);
}
//}
}
client.flush();
if ((inString.length())>5)
{
//Serial.print("inString: ");
//Serial.println(inString);
if (inString.contains("Address"))
{
int from=(inString.indexOf("Address")+9);
int lunghe=inString.length();
int to=(lunghe-16);
/*Serial.print("Lunghezza instring = ");
Serial.println(lunghe);
Serial.print("Posizione address + 9 = ");
Serial.println(from);
Serial.print("Posizione fine - 16 = ");
Serial.println(to);
*/
//strcpy(ipadsl,(inString.substring((inString.indexOf("Address")+9),(inString.length()-16))));
ipadsl=inString.substring(from,to);
//Serial.print("Lunghezza ipadsl = ");
//Serial.println(ipadsl.length());
Serial.print("IP rilevato dal sito: >");
Serial.print(ipadsl);
Serial.println("<");
}
}
if (!client.connected())
{
Serial.println("disconnecting.");
client.stop();
delay (1000);
Serial.print("lunghezza IP ");
//Serial.println(strlen(ipadsl));
Serial.println(ipadsl.length());
if ((strlen(ipadsl))!=0)
{
Serial.print("IP nuovo : >");
Serial.print(ipadsl);
Serial.println("<");
for (int i=0; i<(ipadsl.length()); i++) { //salva in memoria l'indirizzo acquisito
ipadslold[i] = EEPROM.read(i);
//Serial.print("carattere : >");
//Serial.print(ipadslold[i]);
//Serial.println("<");
}
Serial.print("IP vecchio: >");
Serial.print(ipadslold);
Serial.println("<");
if (strcmp(ipadsl,ipadslold))
{
Serial.println("IP diverso PUBBLICO");
digitalWrite(ledR, HIGH);
pubblicaip();
digitalWrite(ledR, LOW);
}
else
{
Serial.println("IP uguale");
}
digitalWrite(ledG, LOW);
//ipadslold="";
//ipadslold.append(ipadsl);
//ipadslold="";
//Serial.print("IP vecchio azzerato: >");
//Serial.print(ipadslold);
//Serial.println("<");
//strcpy(ipadslold,ipadsl);
for (int i=0; i<(ipadsl.length()); i++) { //salva in memoria l'indirizzo acquisito
EEPROM.write(i, ipadsl[i]);
}
}
}
}
void pubblicaip()
{
int timeout=0;
Serial.print("connecting to ");
Serial.println(ip_to_str(domaindydns));
Serial.print("IP da pubblicare ");
Serial.println(ipadsl);
if (clientdyn.connect()) {
Serial.println("connected");
clientdyn.print("GET /nic/update?hostname=");
clientdyn.print(hostname);
clientdyn.print("&myip=");
clientdyn.print(ipadsl);
clientdyn.println(" HTTP/1.0 ");
//clientdyn.println("Host: members.dyndns.org ");
clientdyn.print("Host: ");
clientdyn.println(ip_to_str(domaindydns));
clientdyn.print("Authorization: Basic ");
clientdyn.println(userpwdb64);
clientdyn.println("User-Agent: futura - arduinodydns - 1.1");
clientdyn.println();
} else {
Serial.println("connection failed");
}
// delay(3000);
while (!clientdyn.available() && timeout<50)
{
timeout++;
Serial.print("Time out ");
Serial.println(timeout);
delay(100);
}
while (clientdyn.available())
{
if (clientdyn.available())
{
char c = clientdyn.read();
Serial.print(c);
}
}
if (!clientdyn.connected())
{
Serial.println();
Serial.println("disconnecting.");
clientdyn.stop();
}
}
// This is just a little utility function to format an IP address as a string.
const char* ip_to_str(const uint8_t* ipAddr)
{
static char buf[16];
sprintf(buf, "%d.%d.%d.%d\0", ipAddr[0], ipAddr[1], ipAddr[2], ipAddr[3]);
return buf;
}
Download the DDNS sketch for Arduino
BOM
<span style="font-family: Consolas, Monaco, 'Courier New', Courier, monospace; font-size: 12px; line-height: 18px; white-space: pre;">R1, R2: 470 ohm</span> <span style="font-family: Consolas, Monaco, 'Courier New', Courier, monospace; font-size: 12px; line-height: 18px; white-space: pre;">R3: 10 kohm</span> C1: 100 nF C2: 470 μF 25 VL C3: 100 nF C4: 470 μF 16 VL C5: 15 pF C6: 15 pF C7: 100 nF U1: WIZNET U2: ATMEGA328P (with Arduino bootloader) U3: LD1086V33 P1: Microswitch LD1: LED 3 mm yellow LD2: LED 3 mm red Q1: Quarzo 16 MHz D1: 1N4007 power jack Dip socket 14+14 Break away headers male 6 via Break away headers female 2x10 via (2 pz) |
















Pingback: Electronics-Lab.com Blog » Blog Archive » Arduino DDNS (Dynamic DNS)
Pingback: Arduino DDNS (Dynamic DNS) | Tehnik Service
Pingback: Arduino DDNS (Dynamic DNS) | LED World
Pingback: Dynamic DNS updating – no PC required - machine quotidienne
Pingback: Dynamic DNS updating – no PC required | House of Mods
Pingback: Arduino DDNS (Dynamic DNS) by Open-Electronics.org – maker.wiznet.io
Pingback: 3pictures